Overview of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the highest incidence of cancer in China, and its incidence rate and mortality rate are the first. 787000 new cases of lung cancer accounted for 20.03% of the total new cases. 631000 lung cancer deaths accounted for 26.99% of the total deaths. According to the degree of differentiation, morphological characteristics, and biological characteristics of lung cancer, it is currently divided into two major categories, namely small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, which include squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, large cell carcinoma, etc.
The pathogenesis of lung cancer is not yet fully understood, but there is evidence that the occurrence of lung cancer is related to factors such as smoking, air pollution, occupational carcinogens, diet, genetics, etc. Overall, both genetic and environmental factors are involved in its onset.
The relationship between pulmonary nodules and lung cancer
Pulmonary nodules refer to solitary, well-defined nodules with a diameter of less than or equal to 3cm and surrounded by aerated lung tissue. A pulmonary nodule with a diameter less than or equal to 1cm is called a pulmonary nodule. The common causes of pulmonary nodules are tumors, infectious granulomas, congenital lesions, etc. There are cancerous nodules less than 8mm, and benign nodules greater than 8mm. Some patients with early lung cancer present as pulmonary nodules. Tracking studies have shown that a small nodule can gradually become cancer after ten to twenty years. Once a pulmonary nodule is discovered, regular follow-up is recommended. Due to the clear correlation between tumor size and staging and prognosis, rapid identification of benign and malignant lung nodules, removal of malignant lesions, avoidance of unnecessary benign lesion resection, and reduction of patient economic burden are currently hot topics in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
Clinical significance of lung cancer MRD detection
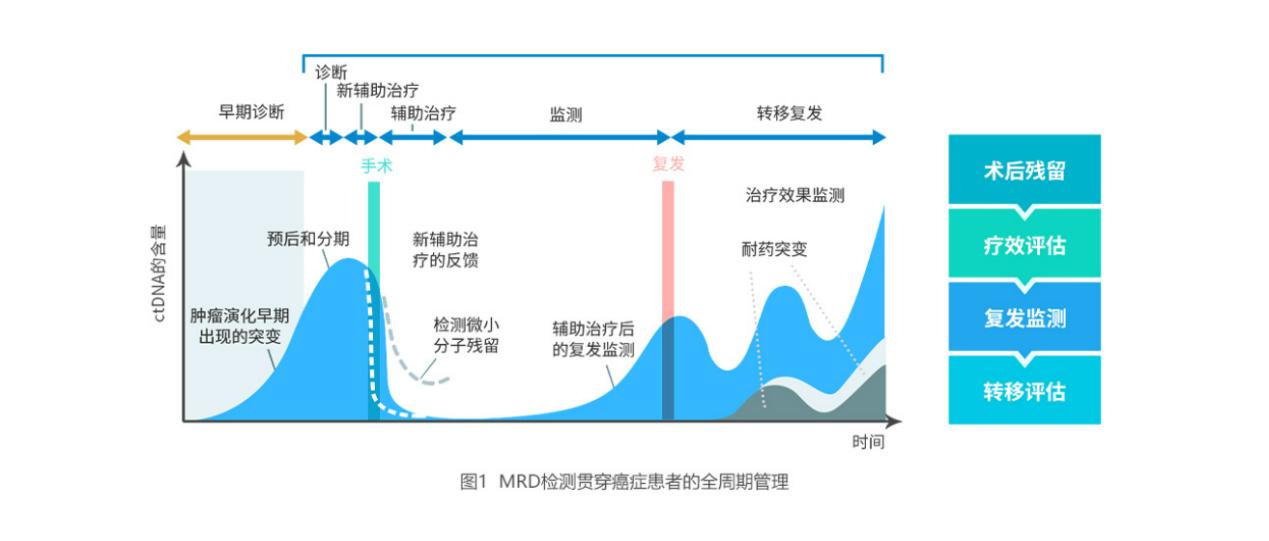
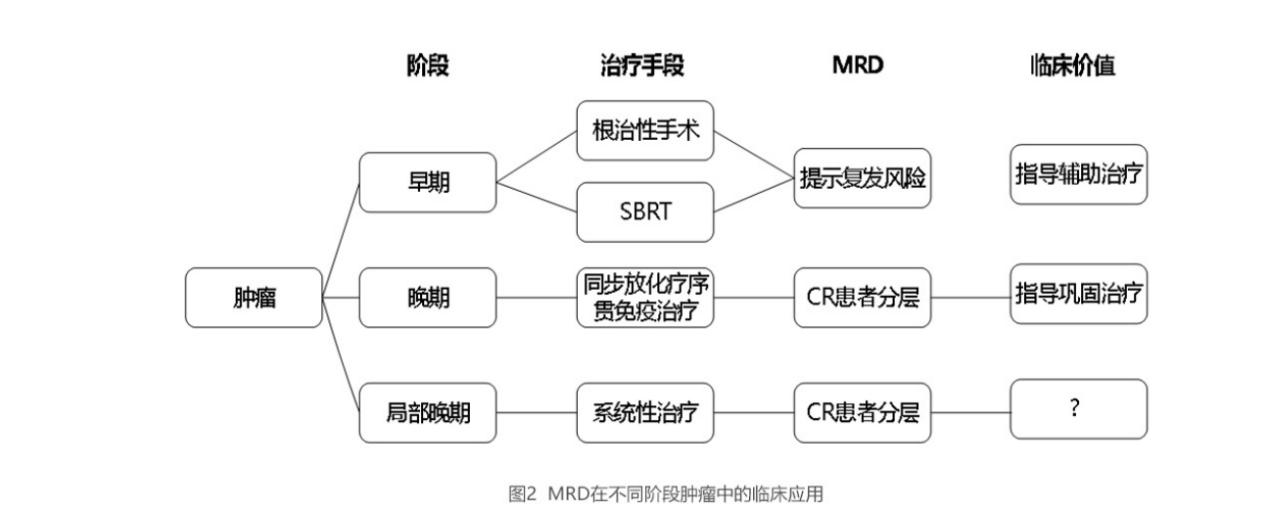
Minimal residual disease (MRD) refers to a small amount of cancer cells remaining in the body after cancer treatment, which cannot be detected by traditional imaging (including PET/CT) or laboratory methods. However, MRD releases circulating cell free tumor DNA (ctDNA). Therefore, based on the ctDNA/cfDNA methylation and other omics panels, the application of liquid biopsy technology [1] can track MRD. Detection and tracking of MRD can more accurately support cancer treatment decisions compared to traditional clinical or imaging methods. By identifying abnormal molecules from cancer sources, predicting the persistence and clinical progression of MRD, the entire process management of postoperative residual, efficacy evaluation, recurrence detection, and metastasis evaluation in cancer patients can be achieved [2] (Figure 1) (Figure 2)